显然,将新数据插入到数据库与从数据库中取回数据是相似的。我们可以遵循同样的基本步骤——建立一个连接、发送查询,最后检查结果。在这种情况中,发送的查询是INSERT而不是SELECT。
尽管这些处理过程非常类似,但是通过一个例子来了解二者的区别是非常有意义的。在图11-3中,可以看到一个基本HTML表单,它可以用来在数据库中输入新的图书。
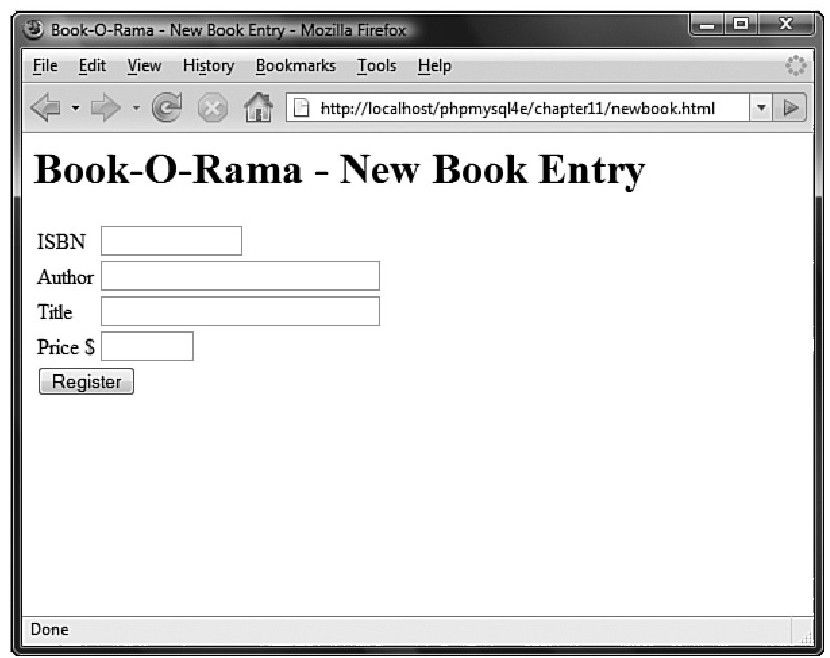 图 11-3 输入新图书到数据库的界面,可供Book-O-Rama职员使用
图 11-3 输入新图书到数据库的界面,可供Book-O-Rama职员使用该页面的HTML源代码如程序清单11-3所示。
该表单的结果将传递给insert_book.php,此脚本接收图书细节,执行一些小的验证,并尝试将数据写入到数据库中。其代码如程序清单11-4所示。
程序清单11-3 newbook.html——图书输入页的HTML
<html>
<head>
<title>Book-O-Rama-New Book Entry</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Book-O-Rama-New Book Entry</h1>
<form action=\"insert_book.php\"method=\"post\">
<table border=\"0\">
<tr>
<td>ISBN</td>
<td><input type=\"text\"name=\"isbn\"maxlength=\"13\"size=\"13\"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Author</td>
<td><input type=\"text\"name=\"author\"maxlength=\"30\"size=\"30\"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Title</td>
<td><input type=\"text\"name=\"title\"maxlength=\"60\"size=\"30\"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Price$</td>
<td><input type=\"text\"name=\"price\"maxlength=\"7\"size=\"7\"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=\"2\"><input type=\"submit\"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
程序清单11-4 insert_book.php——该脚本将新的图书写入到数据库
<html>
<head>
<title>Book-O-Rama Book Entry Results</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Book-O-Rama Book Entry Results</h1>
<?php
//create short variable names
$isbn=$_POST[\'isbn\'];
$author=$_POST[\'author\'];
$title=$_POST[\'title\'];
$price=$_POST[\'price\'];
if(!$isbn||!$author||!$title||!$price){
echo\"You have not entered all the required details.<br/>\"
.\"Please go back and try again.\";
exit;
}
if(!get_magic_quotes_gpc){
$isbn=addslashes($isbn);
$author=addslashes($author);
$title=addslashes($title);
$price=doubleval($price);
}
@$db=new mysqli(\'localhost\',\'bookorama\',\'bookorama123\',\'books\');
if(mysqli_connect_errno){
echo\"Error:Could not connect to database.Please try again later.\";
exit;
}
$query=\"insert into books values
(\'\".$isbn.\"\',\'\".$author.\"\',\'\".$title.\"\',\'\".$price.\"\')\";
$result=$db->query($query);
if($result){
echo$db->affected_rows.\"book inserted into database.\";
}else{
echo\"An error has occurred.The item was not added.\";
}
$db->close;
?>
</body>
</html>
成功插入一本书的结果如图11-4所示。
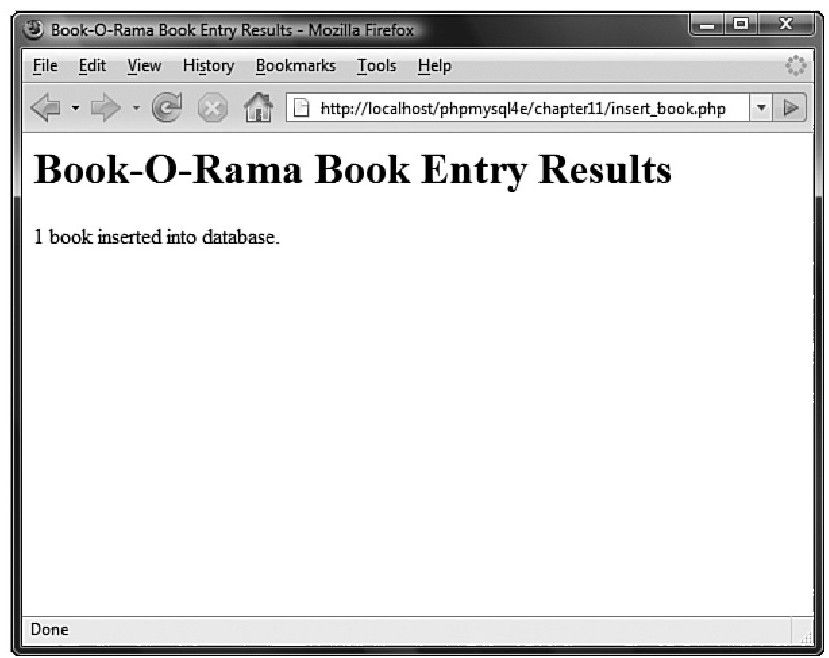 图 11-4 脚本完成任务并报告图书已经被添加到数据库中
图 11-4 脚本完成任务并报告图书已经被添加到数据库中如果看看insert_book.php的代码,可以发现其中许多代码都与从数据库中取回数据的脚本相似。我们已经验证所有表格字段都已经填满,并调用addslashes函数(如果是必需的)正确地将数据格式化,以便插入数据库:
if(!get_magic_quotes_gpc){
$isbn=addslashes($isbn);
$author=addslashes($author);
$title=addslashes($title);
$price=doubleval($price);
}
当价格以浮点数的形式保存在数据库时,我们不希望在小数点的前后插入斜杠。通过调用doubleval函数,可以对该数字字段进行过滤,从而去除所有临时字符。该函数在第1章中讨论过。也要注意用户可能输入的任何货币符号。
在这里,我们再次通过实例化mysqli对象来连接数据库,而且设置了一个发送给数据库的查询。在这个例子中,该查询是一个SQL INSERT操作:
$query=\"insert into books values
(\'\".$isbn.\"\',\'\".$author.\"\',\'\".$title.\"\',\'\".$price.\"\')\";
$result=$db->query($query);
通过调用$db->query(或者mysqli_query,如果希望使用面向过程风格的方法),该查询将以常见的方式在数据库上执行。
使用INSERT和SELECT的一个显著不同之处在于对mysqli_affected_rows的使用,这是一个过程式版本的函数或者面向对象版本中的一个类成员变量:
echo$db->affected_rows.\"book inserted into database.\";
在前面的脚本中,我们使用mysqli_num_rows来确定SELECT操作可以返回多少行记录。
当编写一个修改数据库的查询时,例如INSERT、DELETE和UPDATE,应该使用mysqli_affected_rows函数。
到目前为止,我们已经介绍了通过PHP使用MySQL数据库的基础知识。
